5.11.3. Flow Analysis at the Institute of Chemistry, University in Bialystok
Anatol Kojlo
The research in the field of flow analysis were initiated at the Department of Analytical Chemistry, Institute of Chemistry, University in Bialystok (UB) in 1986 as a result of the scientific collaboration between Helena Puzanowska-Tarasiewicz and Anatol Kojlo with Marek Trojanowicz from the Faculty of Chemistry, Warsaw University. Thanks to the Trojanowicz's experience and assistance it was possible to build and use first flow injection systems and carry out experiments. In addition, in 1988 a contact has been made with Jose Martinez Calatayud from Valencia University (Spain), who performed research on adaptation of FIA to pharmaceutical analysis. This resulted in cooperation including, publication and conference presentations. Collaboration with S?awomir Kalinowski from the University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn involved investigation of various detection systems for flow analysis. The research "flow" team, headed at first by Helena Puzanowska-Tarasiewicz and then by Anatol Kojlo was composed over the years of the following persons: Elzbieta Wolyniec, Jacek Michalowski, Jerzy Póltorak, Julita Malejko, Edyta Nalewajko-Sieliwoniuk and Piotr Halaburda (Fig.1).
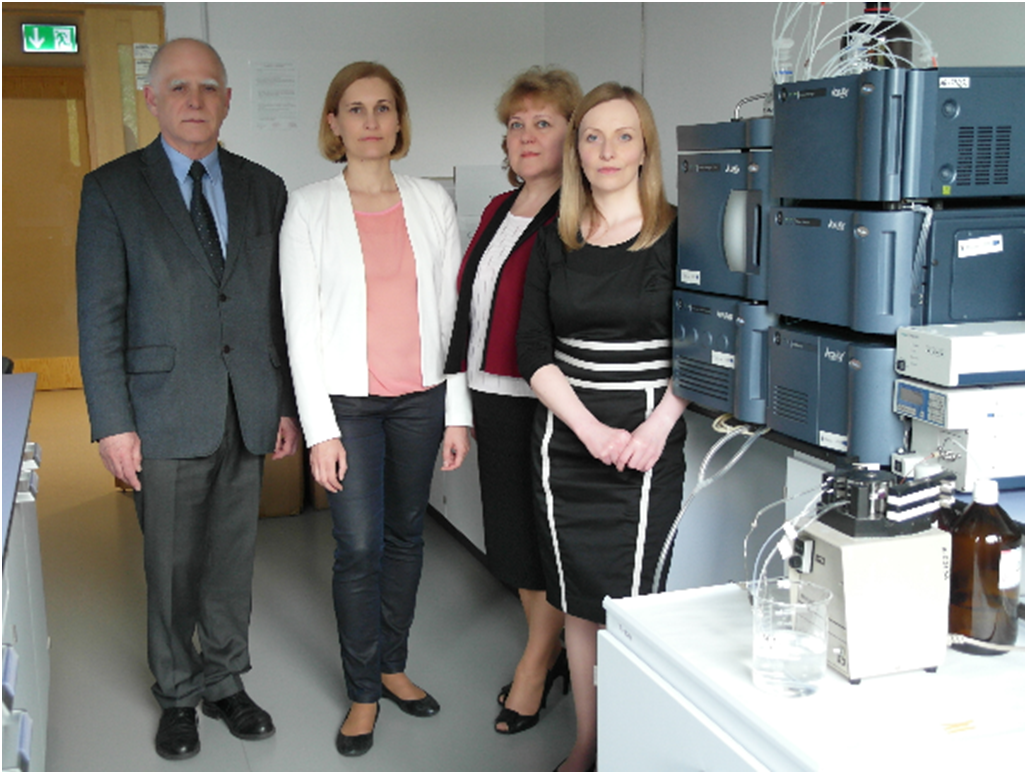

Fig. 1. Anatol Kojlo's research team; from left to right: Anatol Kojlo, Edyta Nalewajko-Sieliwoniuk, Elzbieta Wolyniec i Julita Malejko
The first work on Flow Injection Analysis was determination of sulphates in natural waters [1]. Next research area was focused environmental assay . In particular, two flow systems were designed and applied to assay of traces of phenols using reactions of phenols with 4-aminopirine and with diozotizated p–nitroaniline [2]. Phenols were also fivefold preconcentrated and determined in natural waters with the use of multicommutated flow injection system equipped with a column containing XAD-4 resin and with a chemiluminescence detector [3]. A competitive flow method for simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of nitrates and nitrites was also developed [4]: due to the special construction of the flow system it was able to determine both analytes on the basis of maximum and inflection points of a single injection peak.
Attempts were made to develop the flow procedures for determination of platinum and other planetoids emitted into the environment (from e.g. car catalysts) and therefore present in dust samples and samples of river and spring waters. The interesting approach was based on catalytic effect of platinum ions on the reaction of oxidation of luminal and on on-line separation of analyte on the column containing green algae Chlorella vulgaris immobilized on Cellex-T support [5].
In the cycle of works connected with pharmaceutical and clinical analysis, a number of flow injection systems with spectrophotometric, spectrofluorimetric, chemiluminescence and biamperometric detection were designed dedicated to the determination of phenotiazine, catecholamine, amino acids, and ascorbic acid in pharmaceutical and biological samples. In particular, the FIA systems equipped with column solid-phase reactors of manganese dioxide or lead dioxide in¬corporated in polyester resin beads were used for the determination of adrenaline [6] and phenothiazine derivatives [7]. In another system chlorpromazine was potentiometrically determined on the basis of its reaction with lead dioxide entrapped into polymeric material in a packed-bed reactor [8]. A novel strategy for the preparation of solid-phase reactors by ''impregnation'' of a poly(vinyl chloride) coil with the reagent was carried out and applied to the fluorimetric flow injection determination of adrenaline [9].
In the separate cycle of flow examinations different analytical problems with food analysis were solved. In particular, a novel method was developed for the determination of the total polyphenol index of plant-derived foods basing on chemiluminescence Mn(IV)-formaldehyde-hexametaphosphate system [10]. In order to enhance automation of this procedure, the FIA system was replaced first by a multicommutated flow system [11] and next the multi-pumping flow system equipped with direct-injection detector [12]. Due to these approaches the consumption of energy, reagents, and wastes was substantially reduced.
Recently, the method for simultaneous post-column determination of polyphenolic antioxidants in extracts from leaves of Cirsium palustre based on HPLC combined with flow injection chemiluminescence detection has been developed [13]. As a result of this research it was possible to define the quantitative and qualitative composition of polyphenols present in herbs of Asteracea family, which hitherto were used only in folk medicine.
The scientific results of the Kojło’s team are more than 50 “flow”articles, 5 PhD theses, and more than 60 master’s theses.